Understanding the Importance of Dealing with Anxiety
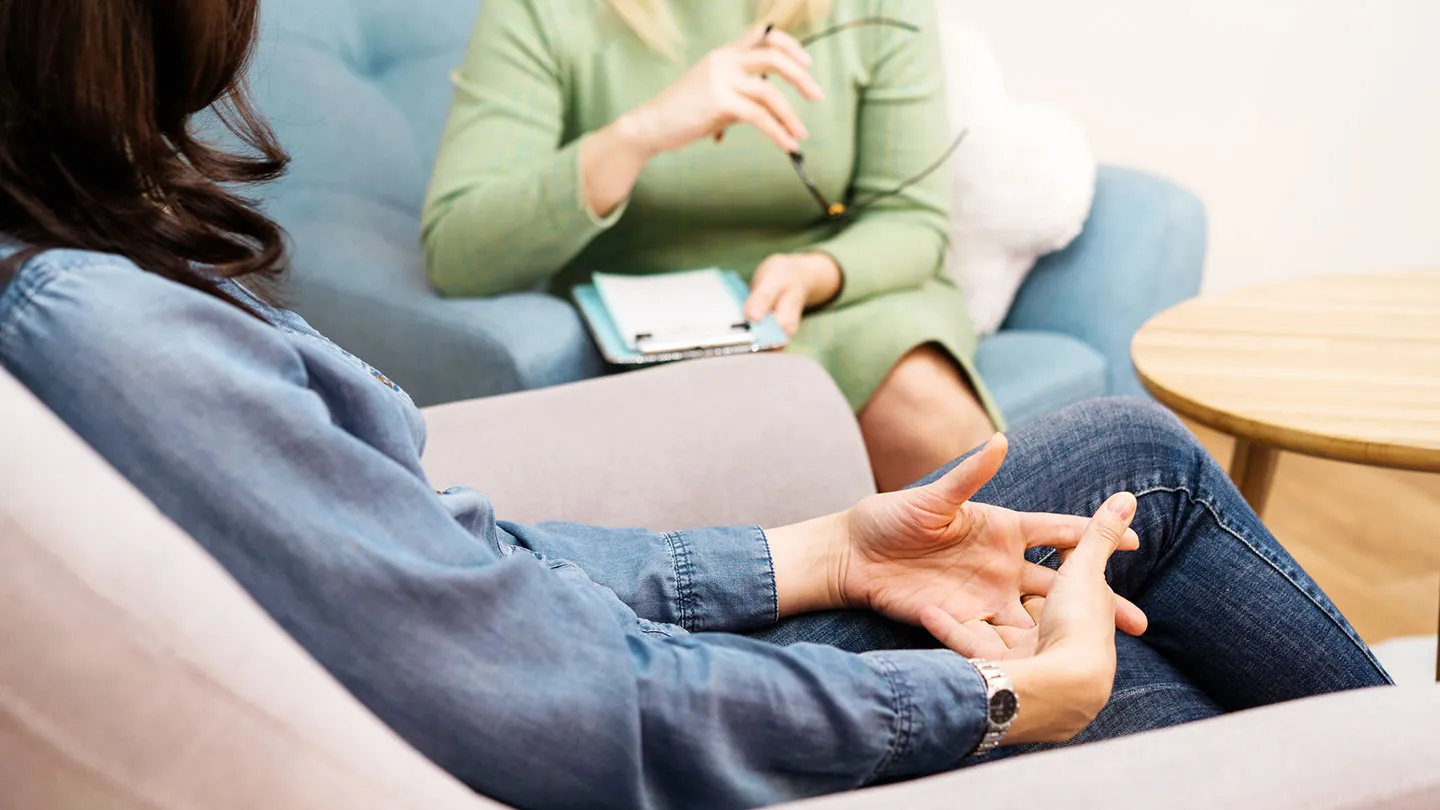
Dealing with anxiety is a crucial step in improving overall mental health and emotional stability. Anxiety often manifests through excessive worry, restlessness, and physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat or muscle tension. Without effective management, these symptoms can interfere with daily life, work performance, and relationships. By learning structured approaches to Dealing with anxiety, individuals can develop healthier thought patterns, gain emotional resilience, and enhance their quality of life.
What Cognitive Behavioral Techniques Mean in Dealing with Anxiety
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is one of the most widely recognized psychological treatments for dealing with anxiety. CBT focuses on the connection between thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. When individuals experience anxious thoughts, they often develop negative beliefs and avoidant behaviors, which fuel the cycle of anxiety. Through cognitive behavioral techniques, people can identify harmful thought patterns, challenge them, and replace them with healthier alternatives. This approach makes dealing with anxiety more structured and effective.
Identifying Negative Thought Patterns When Dealing with Anxiety
The first step in using CBT for dealing with anxiety is recognizing the automatic negative thoughts that trigger worry. Many people experience “catastrophic thinking,” where they assume the worst outcome in any situation. Others engage in self-critical thoughts that lower confidence and increase fear. By writing down these thoughts and evaluating their accuracy, individuals can start dealing with anxiety more logically. Understanding that not every thought is factual is essential in regaining control.
Challenging Irrational Beliefs in Dealing with Anxiety
Once negative thoughts are identified, the next step in dealing with anxiety is to challenge them. For example, if someone believes they will fail a presentation, they can ask themselves what evidence supports that belief and what evidence disproves it. Often, irrational beliefs lack factual support. By reframing these thoughts with rational and balanced perspectives, individuals weaken the power of anxiety. This cognitive restructuring is a cornerstone of dealing with anxiety through CBT.
Behavioral Techniques for Dealing with Anxiety
Alongside cognitive restructuring, CBT emphasizes behavioral strategies to support dealing with anxiety. Avoidance is a common behavior among people with anxiety, but it often strengthens the fear. Instead, exposure techniques encourage individuals to gradually face feared situations in a safe and controlled way. For example, someone afraid of social gatherings can start by attending small events and gradually build up to larger ones. This process teaches the brain that feared situations are manageable, making dealing with anxiety more effective.
Relaxation and Breathing Exercises for Dealing with Anxiety
Physical symptoms often accompany anxiety, and managing these is essential. Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation are proven tools for dealing with anxiety. These exercises calm the nervous system and reduce physical tension. Practicing them daily helps individuals stay grounded during stressful moments. When paired with cognitive restructuring, relaxation techniques enhance the overall effectiveness of dealing with anxiety.
Journaling as a Tool for Dealing with Anxiety
Journaling is another powerful method for dealing with anxiety using CBT principles. Writing down worries provides a safe outlet for emotions and helps clarify patterns of negative thinking. Individuals can track situations that trigger anxiety, their automatic thoughts, and healthier alternatives they use to replace them. Over time, this reflective practice strengthens coping strategies and reinforces progress in dealing with anxiety.
Problem-Solving Skills in Dealing with Anxiety
Many individuals with anxiety struggle with uncertainty and decision-making. CBT teaches structured problem-solving to break overwhelming challenges into manageable steps. For example, instead of worrying about a large project, one can divide it into smaller, achievable tasks. This approach reduces the feeling of being stuck and increases confidence. Applying problem-solving skills regularly is a practical way of dealing with anxiety in daily life.
The Role of Self-Compassion in Dealing with Anxiety
While CBT emphasizes logical thinking, self-compassion also plays a vital role in dealing with anxiety. People often criticize themselves harshly for feeling anxious, which worsens emotional distress. Learning to treat oneself with kindness and understanding reduces shame and creates a supportive inner dialogue. When combined with cognitive and behavioral techniques, self-compassion enhances long-term success in dealing with anxiety.
Long-Term Benefits of Dealing with Anxiety Through CBT
The benefits of CBT extend far beyond immediate relief. Individuals who commit to these techniques often experience improved self-awareness, better emotional regulation, and enhanced problem-solving abilities. Over time, dealing with anxiety through CBT fosters resilience, allowing people to handle future stressors more effectively. Instead of being controlled by fear, they develop confidence in their ability to face life’s challenges.
Conclusion: A Practical Approach to Dealing with Anxiety
Dealing with anxiety requires both mental and behavioral changes, and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy provides a structured path toward healing. By identifying negative thoughts, challenging irrational beliefs, practicing relaxation, and applying problem-solving skills, individuals gain the tools to overcome fear and worry. Journaling and self-compassion further strengthen these efforts, ensuring that dealing with anxiety becomes a sustainable and empowering process. With commitment and practice, anyone can transform anxious thinking into a foundation for mental well-being.